If the same idea was used in gene selection, then the selected signature gene lists would be similar for different studies. Thus, there is a strong possibility that gene selections were influenced by variations in sample collection, sample size, data processing, and microarray platform. Our method does not use survival time as a parameter for gene selection; rather, it used a gene clustering approach instead of group statistics. It is not unexpected that our gene list does not overlap previously reported lung cancer signature genes as our signature development approach is quite different. The ratio of 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid two-gene expression within an individual patient has been reported as a biomarker signature development in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis as well as for breast cancer prognosis. The single two-gene ratio or geometric mean of several two-gene ratios was selected between the treatment failures and the treatment responders from the training data samples. The single two-gene ratio works well for cancer cell type classification or diagnosis; for example, between malignant pleural mesothelioma and adenocarcinoma, but it may not be able to reflect the complex tumor progression process for prognosis. In some cases, there could be substantial variation of the two genes among different samples. Therefore 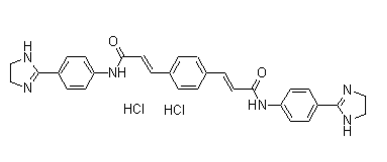 many new studies in recent years still rely on the Cox regression modeling to build the prognostic signatures. Most of these models applied the gene expression value to the Cox proportional coefficient of each signature gene and combined them as the patient risk scores. Some models computed the probability of a patient falling into the low-risk or high-risk class as the patient risk scores. However, there are difficulties in using overall survival as an endpoint in prognostic modeling in cancer. The expression variations of the same gene among individual subjects are substantial. Some genes associated with other aggressive diseases may be present in a subject’s tumor. Similarly, a subject might develop and succumb to some other clinical condition shortly after diagnosis. In these instances, no correlation exists between gene expression and subject survival. The complex models could learn the expression variable as well as other variations precisely, which would result in low reproducibility if used for a different data set. Instead, we return to the two-group gene expression ratio approach but select these two groups of genes using differences between normal lung cells and lung cancer cells that represent the whole Yin and Yang effects of the cell. Among the Yin genes we selected included pathways and networks connected to the canonical Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer pathway. The Yang genes are connected to the Retinoic acid receptor activation pathway and the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation pathway. RAR activation induces cell differentiation and may antagonize cancer progression because retinoic acid or vitamin A is required for the differentiated state of normal cells. Hepatic Stellate Cells play a key role in the storage and transport of retinoids and the lung tissue harbors the Hepatic Stellate-like cells. These two pathways alter the balance between Yin and Yang, consequently altering patient survival. A useful prognostic signature should not only predict the patient’s prognosis, but should also help clinical therapeutic Salvianolic-acid-B decision making. Although surgery is a standard treatment for early stage lung cancer, more than 20% of stage I patients will relapse. This cohort of patients may benefit from chemotherapy.
many new studies in recent years still rely on the Cox regression modeling to build the prognostic signatures. Most of these models applied the gene expression value to the Cox proportional coefficient of each signature gene and combined them as the patient risk scores. Some models computed the probability of a patient falling into the low-risk or high-risk class as the patient risk scores. However, there are difficulties in using overall survival as an endpoint in prognostic modeling in cancer. The expression variations of the same gene among individual subjects are substantial. Some genes associated with other aggressive diseases may be present in a subject’s tumor. Similarly, a subject might develop and succumb to some other clinical condition shortly after diagnosis. In these instances, no correlation exists between gene expression and subject survival. The complex models could learn the expression variable as well as other variations precisely, which would result in low reproducibility if used for a different data set. Instead, we return to the two-group gene expression ratio approach but select these two groups of genes using differences between normal lung cells and lung cancer cells that represent the whole Yin and Yang effects of the cell. Among the Yin genes we selected included pathways and networks connected to the canonical Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer pathway. The Yang genes are connected to the Retinoic acid receptor activation pathway and the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation pathway. RAR activation induces cell differentiation and may antagonize cancer progression because retinoic acid or vitamin A is required for the differentiated state of normal cells. Hepatic Stellate Cells play a key role in the storage and transport of retinoids and the lung tissue harbors the Hepatic Stellate-like cells. These two pathways alter the balance between Yin and Yang, consequently altering patient survival. A useful prognostic signature should not only predict the patient’s prognosis, but should also help clinical therapeutic Salvianolic-acid-B decision making. Although surgery is a standard treatment for early stage lung cancer, more than 20% of stage I patients will relapse. This cohort of patients may benefit from chemotherapy.
Monthly Archives: May 2019
Receptor blockade could potentially also enhance the protective immune responses of susceptible individuals
Development of ICU-AW is associated with increased mortality and short- and long term morbidity. Currently, no specific treatments for ICU-AW exist. For future treatments to be successful, timing may be of importance. The first signs of ICUAW can be found starting from day 2 after admission when decreased excitability of muscle and nerve can be observed. Initiation of treatment at this moment may be more effective because the observed abnormalities may still be reversible. Such early treatment would require an early diagnosis of ICUAW. At present, the diagnosis of based on clinical examination using manual muscle strength assessment. In most critically ill patients, manual muscle strength assessment is not possible early in the disease course due to impaired consciousness or attentiveness. A solution to this diagnostic delay may be to quantify the risk that a patient will develop using a prediction model early after ICU admission. ICUCAW is associated with several risk factors, including sepsis, the presence of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome and severity of illness. We hypothesized that early prediction of possible and reliable. To investigate this, we built a prediction model based on previously identified risk factors. Other, more technically demanding, methods for early prediction of ICU-AW have also been investigated. Weber-Carstens et al studied early electrophysiological testing and found a sensitivity of 83% and specificity of 89% for direct muscle stimulation. This is indicative of a better discriminative performance than our prediction model, but electrophysiological studies in general, and direct muscle stimulation in particular, are technically demanding and are not widely available in ICUs. Diagnostic potential of other methods for an early diagnosis of ICU-AW, like ultrasound or biological markers, has been scarcely studied. The ability to predict ICU-AW early after ICU admission and circumvent this limitation of muscle strength assessment as a diagnostic method can be an important step in critical care and research. A study by Haas et al., in which the authors examined genome-wide expression in P. infestans over four time points from 2 to 5 dpi of potato, revealed similar results that in general RXLRs showed early expression. Interestingly, the elicitin class showed the induction at GC and infection stages for P. capsici, whereas there were no elicitins induced at all during infection by P. infestans. The larva ecloses and immediately feeds on the pedestal. Second, the larvae then systematically alternate between feeding on the walls of the egg chamber and their own frass. Many dung beetle researchers have considered this second stage of coprophagy to be a method for further extracting the nutrients from their frass. However, we hypothesize that the larva may acquire their microbiome from the pedestal and brood ball walls. During self-coprophagy, the larva may be selecting for or concentrating the microbes that facilitate their digestion of the dung the female provides. Similarly, in other cellulose degrading taxa, such as wood roaches, juveniles do not survive unless they ingest frass from parents that have the microbiota needed for digestion. No microbes or matrix were seen on the Ginsenoside-F4 surface of the dung beetle egg. PCR amplicons were not produced when DNA from the egg was used as a template. Lack of amplification is never a definitive result.
The endometrial stroma of the uterus, peroredoxins has been reported to be present in the mouse ooplasm of primary follicles
It is possible that peroxiredoxins also function similarly in rabbits. The results of this study showed that peroxiredoxins 1 and 2 were upregulated in rES cells. The high peroxiredoxin levels in rabbit ES cells may be associated with their active proliferation capacity and at least partially linked to their future differentiation competency. However, Western blot analysis and immunocytochemistry failed to confirm a similar upregulation in rES cells. Reasons for this discrepancy are unclear, but it could be due to the stressful in vitro culture conditions, which might have leveled up its expressions in all three cell types, or the co-existence of other isoforms detected in this study which warrant further investigation. Heat shock proteins are ubiquitously expressed, and are transcriptionally regulated under physiological and stressful conditions such as elevated temperatures, oxygen tension and chemical insults. The best characterized roles of HSPs are the involvement of chaperone-mediated protein folding. In the mouse, downregulation of HSPs and the co-chaperones in mES cell lines upon differentiation was observed. Proteomic analysis of this study showed that two protein spots of HSP60 were highly expressed in rES rather than in fibroblast cells. Western blot and immunocytochemical analyses both confirmed the 2-DE results. HSP60 has been known to bind directly with the Oct4 and Nanog genes which directly Catharanthine sulfate regulate Oct4 and other stemness genes involving the differentiation of adipose tissuederived stem cells in Gomisin-D humans. The finding in this study confirmed the observations in previous study that undifferentiated cells expressed more HSPs which might be attributable to their active protein synthesis or maintaining pluripotency-related cellular activities, compared to the terminally differentiated cells in the relatively quiescent state. The expression of HSP90 was only upregulated in f-rES cell lines and showed similar lower levels in fibroblasts and p-rES cells based on our 2-DE analyses. It has been reported that the chaperoning activity of HSP90 depends on its ability to hydrolyze ATP and its potential to form stable complexes with HSP70 and HSP70/HSP90/organizing protein in fertilized mouse embryo-derived ES cells. The HOP is a 60 kDa co-chaperone that binds and regulates the activity of chaperones. Using RNAi to knockdown HOP in mES cell lines caused 68% depletion of STAT3 mRNAs, downregulated soluble phosphotyrosine-STAT3 levels, and leading to an extranuclear accumulation of STAT3, which ultimately reduced Nanog mRNA levels and lost the ability to form embryoid bodies. These studies confirmed the previous work showing that HSP90 interacted with the JAK/STAT3 signaling molecules in somatic cells. The HSP90 was reported to complex with STAT3 in human embryonic kidney carcinoma cells. Western blot analysis did not completely confirm the differential expression of HSP90 observed in 2-DE analysis in different cell types. The discrepancy was unclear. In general, HSP90 was upregulated in both f-rES cells and p-rES cells, but remained low in fibroblasts. It might be due to the passage number of rES cells used for analysis, or the commercially available HSP90 antibodies recognized different isoforms  of HSP90. However, it has been reported that HSP90 was upregulated in both f-rES and p-rES cells, where the involvement of the proteostatic maintenance of onco-proteins or stemness were demonstrated. Recently, it was also reported that LIF promotes the interaction of HSP90 with STAT3 for maintenance of self-renewal in mES cells. These works provide strong supportive evidence to our previous and current proteomics findings.
of HSP90. However, it has been reported that HSP90 was upregulated in both f-rES and p-rES cells, where the involvement of the proteostatic maintenance of onco-proteins or stemness were demonstrated. Recently, it was also reported that LIF promotes the interaction of HSP90 with STAT3 for maintenance of self-renewal in mES cells. These works provide strong supportive evidence to our previous and current proteomics findings.
Next the ability of parasites to form a TJ was analysed as described above for myoA KO parasites
Although it has been reported that TJ formation is not blocked upon interference with parasite actin, we found in pulse invasion assays that only of all parasites were capable of establishing a TJ, when compared to control parasites. This result fits well with the overall reduction in the invasion rate of act1 KO parasites. It was thus concluded that act1 KO parasites are capable of penetrating host cells upon TJ formation, and that a step upstream of TJ formation is blocked in the absence of Act1. Iscussion Apicomplexan parasites have evolved unique organelles and structures to actively invade the host cell. Conditional knock out is a powerful approach to decipher function of a given protein by deleting a gene in a tissue or time specific manner. In response to metabolic challenges, the placenta may adapt its functional capacity by modifying its morphology and/or nutrient transporter activity and, thereby, could contribute to the developmental programming of disease susceptibility of the offspring. To date, the molecular mechanisms underlying the modifications of fetal growth in the context of pregnancies complicated with moderate hyperglycemia have not been investigated. As in diabetic pregnancies, the placenta from women with MGH showed vascular dysfunctions and major tissue damage that could affect the placental function and thus compromise fetal development. To our knowledge, there is no relevant model described in the literature for the study of the placenta in relation to fetal growth. Most of the experimental approaches used to generate mild or severe diabetes during pregnancy have relied on the destruction of pancreatic b-cells through the administration of drugs.One exception is Wunderlich et al., who presented an energy model that can be used for almost all human SH2 domains. However the good performance reported seems to be due to some over-training issues. Previous research showed that the correlations between different ligand positions take important role in the binding specificity of the SH2 domains. In recent years, polynomial kernels have been successfully applied to the prediction of DNAprotein interactions. In this paper, we propose domain specific non-linear models for SH2-peptide interactions that are based on support vector machines. As the complexity of the model increases so does the required number of training instances. While modern high-throughput Tubeimoside-I techniques seem to be the perfect solution to the data requirements, they have other issues. The first problem is that techniques like pool oriented peptide arrays do not test individual peptides but pools of peptides with common properties. In a second phase, individual peptides are tested with separate methods. Thus, while these approaches provide information about real interactions, they cannot reliably be used to assess the lack of a domainpeptide interaction. A similar situation occurs with many highdensity peptides arrays where affinities are not reported. Other high throughput approaches like microarrays do report affinities and thus can be used to assess the lack of strong interaction. These approaches suffer, however, from a low signal to noise ratio and therefore produce results that are often inconsistent. For example, in one microarray experiment found that the number of interactions between 11 peptide sequences extracted from protein ErbB1 and 85 SH2 domains is 37.
Demyelination and experimental autoimmune allergic encephalomyelitis have been widely used for studying and remyelination processes in the CNS
An additional or alternative explanation to explain the lack of phenotype in SkgxTgLYPW mice is that after the threshold of signaling inhibition necessary to trigger thymic signaling anomalies has been trespassed, quantitative reductions in signaling are required in order to see further decreases of selection and an increase in severity of arthritis. Since no studies to date have uncovered profound effects of LYP-W620 on thymic selection, an alternative explanation is that TCR signaling in thymocytes might be controlled by multiple redundant phosphatases. LYP-dependent effects might not be detectable in the presence of a dominant regulator such as CD45, which plays a major role  in both positive and negative regulation of TCR signaling in double positive and single positive thymocytes. Throughout its Albaspidin-AA protracted course, alternating deficits of axonal 20S-Notoginsenoside-R2 functions associated with demyelination deteriorates into conduction failure and progressive axonal degeneration, culminating in partial or complete sensory and motor incapacitation. Functional and developmental studies have indicated essential roles for myelin in the rapid conduction of action potentials along thick myelinated axons. Enveloping neurites in a highly compartmented manner, myelin provides an effective shield essential for saltatory propagation of action potentials. There is considerable but conflicting evidence suggesting a stabilizing influence of voltage-activated KV1 currents on the excitability and conductivity of central and peripheral axons. Mediated through channels produced by tetramerization of KV1.1 with 1.2 a subunits, and normally concentrated at the juxta-paranodes, KV1 channels spread to internodes and nodal segments upon demyelination, causing impedance mismatch and disruption of action potential conduction. Accordingly, indiscriminate pharmacological inhibition of K + currents has been shown to restore the electrogenic functions of demyelinated axons, a mechanism that is implicated in some of the ameliorative influence of 4-aminopyridine and its analogues in MS patients. However, emerging evidence from animal studies suggests that the beneficial effects of therapeuticallyrelevant concentrations of 4-AP on axonal physiology are due to its action as a synaptic transmission enhancer. Indeed, low mM concentrations of 4-AP and 3,4-di-aminopyridine greatly facilitate neurotransmission at both excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Of note, several studies also assigned therapeutic effects of 4-AP to its inhibition of immune cell proliferation. Inevitably, such broad-spectrum effects hampers the utilisation of 4-AP for discriminatory restoration of the functionality of demyelinated axons without off target effects. A prevalence of optic neuropathies with functional disruptions during early MS kindled our interest in analysing the importance of KV1 currents in regulating electrophysiological properties of the optic nerve in a cuprizone-induced model of demyelination. The pervasive correlation between inflammatory optic neuropathies and symptoms of clinical MS, manifested by disruptions of visual functions, renders the ON an attractive experimental model. Being an anatomical extension of the forebrain, ON share key features of central myelinated tracts under healthy and disease conditions. Thus, along with the demonstration of myelin loss and a decrease in the axon diameter, our data also provide important insights into demyelination-related changes in the molecular composition of KV1 channels in central axons, which could be of potential relevance to MS and other disease associated with the loss of myelin.
in both positive and negative regulation of TCR signaling in double positive and single positive thymocytes. Throughout its Albaspidin-AA protracted course, alternating deficits of axonal 20S-Notoginsenoside-R2 functions associated with demyelination deteriorates into conduction failure and progressive axonal degeneration, culminating in partial or complete sensory and motor incapacitation. Functional and developmental studies have indicated essential roles for myelin in the rapid conduction of action potentials along thick myelinated axons. Enveloping neurites in a highly compartmented manner, myelin provides an effective shield essential for saltatory propagation of action potentials. There is considerable but conflicting evidence suggesting a stabilizing influence of voltage-activated KV1 currents on the excitability and conductivity of central and peripheral axons. Mediated through channels produced by tetramerization of KV1.1 with 1.2 a subunits, and normally concentrated at the juxta-paranodes, KV1 channels spread to internodes and nodal segments upon demyelination, causing impedance mismatch and disruption of action potential conduction. Accordingly, indiscriminate pharmacological inhibition of K + currents has been shown to restore the electrogenic functions of demyelinated axons, a mechanism that is implicated in some of the ameliorative influence of 4-aminopyridine and its analogues in MS patients. However, emerging evidence from animal studies suggests that the beneficial effects of therapeuticallyrelevant concentrations of 4-AP on axonal physiology are due to its action as a synaptic transmission enhancer. Indeed, low mM concentrations of 4-AP and 3,4-di-aminopyridine greatly facilitate neurotransmission at both excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Of note, several studies also assigned therapeutic effects of 4-AP to its inhibition of immune cell proliferation. Inevitably, such broad-spectrum effects hampers the utilisation of 4-AP for discriminatory restoration of the functionality of demyelinated axons without off target effects. A prevalence of optic neuropathies with functional disruptions during early MS kindled our interest in analysing the importance of KV1 currents in regulating electrophysiological properties of the optic nerve in a cuprizone-induced model of demyelination. The pervasive correlation between inflammatory optic neuropathies and symptoms of clinical MS, manifested by disruptions of visual functions, renders the ON an attractive experimental model. Being an anatomical extension of the forebrain, ON share key features of central myelinated tracts under healthy and disease conditions. Thus, along with the demonstration of myelin loss and a decrease in the axon diameter, our data also provide important insights into demyelination-related changes in the molecular composition of KV1 channels in central axons, which could be of potential relevance to MS and other disease associated with the loss of myelin.