This study also revealed that the hMSCs encapsulated in the Yunaconitine MMP-sensitive hydrogels displayed diminished hypertrophic behaviors leading to reduced matrix calcification. One likely explanation to this finding is the different amount of cartilaginous matrix deposition in the hydrogels. The MMP-sensitive hydrogels accumulated more GAG and collagen than the MMP-insensitive hydrogels. The two major cartilage ECM molecules, proteoglycans and type II collagen, are known to promote and stabilize chondrogenic phenotype and thereby suppress matrix calcification. Proteoglycans also bind and stabilize various growth factors and help maintain prolonged bioactivity of growth factors. Some of these growth factors such as TGFbs are inhibitors of hypertrophic differentiation. Therefore, the higher cartilage matrix content in the MMP-sensitive hydrogels may have contributed to the suppression of hMSC hypertrophy. A previous study by another group shows that longer therefore more complete chondrogenic induction actually expedites hypertrophy of chondrogenically induced MSCs compared to shorter chondrogenic induction. Our previously published work also indicates that compared to poorly Miglitol differentiated cells, more thoroughly differentiated hMSCs result in more significant hypertrophy after in vivo implantation. The correlation between the extent of MSCs chondrogenesis and the propensity of subsequent hypertrophy certainly warrants further investigation. Nevertheless, multiple factors can regulate hypertrophy at the same time. A study also shows that activated RhoA/ROCK signaling, which is associated with cell spreading and cytoskeletal tension, inhibits chondrocyte hypertrophy. We postulate that the spreading of the differentiated hMSCs in the MMP-sensitive hydrogels may have inhibited hypertrophy in this case. The MMP-cleavable peptide sequence used in this study is a target of multiple MMP species. Therefore, even though the MMP13 expression in the MMP-sensitive hydrogels was lower than that in the MMP-insensitive hydrogel, cells were still able to break down the MMP-cleavable crosslinks. However, the exact mechanisms underlying the observed effects of cell-mediated degradation on hMSC chondrogenesis remain to be elucidated. Future study is needed to better understand the mechanism of this regulation of hMSC chondrogenic differentiation by cell-mediated scaffold degradation. In the MMP-sensitive hydrogels, significant cell spreading was only observed after around 10 days of culture. The serum-free media used in this study likely induced less cell MMP synthesis than serum-supplemented media do, in which cell spreading in similar MMP-sensitive hydrogels were observed at earlier time points in an unpublished separate study. It should also be noted that significant variation in MMP expression exists among hMSCs from different donors. The hMSCs used in this study are from a healthy young donor. Our previous experiments revealed that hMSCs from osteoarthritic patients express significantly higher MMPs and would have degraded these HA hydrogels faster. Previous studies suggest that a round cell morphology and disrupted cell cytoskeletal structure is closely associated with chondrogenesis. This appears conflicting to our finding that the more spread hMSCs in the MMP-sensitive hydrogels exhibited better 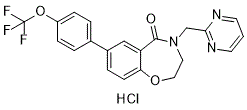 chondrogenesis than the rounded hMSCs in the control group.
chondrogenesis than the rounded hMSCs in the control group.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
A large number of identified and postulated molecular mediators are involved in homeostasis regulation
RVR was found to be the useful 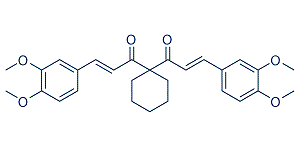 predictor for SVR in treatment of CHC with peg-IFN plus ribavirin. With this aspect in mind, we examined the host genotypes associated with different IFN responses. In patients with RVR, CC genotypes at rs12979860 were present in 77% of the patients whereas the unfavourable CT was present in only 23% of the individuals. Interestingly, none of the patients achieving RVR Talatisamine reported unfavourable TT allele at rs12979860. Similarly, at locus rs8099917, response rates were 73.2% TT, 19.2% TG, followed by 7.6% GG allele. Similar results were obtained in patients with SVR which shows that in 83% of the patients achieving SVR had the favourable CC allele at rs12979860. Interestingly, in patients with relapsed infection it was seen that 66% of the patients had unfavourable CT allele at their rs12979860 locus followed by 34% TT allele. Also at rs8099917, TG genotype was present in 72.4% individuals followed by GG host genotype in 27.6% individuals. Therefore, it could be assumed that favourable genotypes at both rs12979860 and rs8099917 could be important markers for the prediction of the favourable results in patients undergoing IFN therapy in genotype 3 infected patients. Within treatment naive HCV infected individuals, our results showed that the percentage of favourable allele rs12979860 CC and rs8099917 TT was higher; therefore it could be assumed that within our study Mycophenolic acid population the propensity to towards favourable alleles is higher and it could be a valuable input for physicians in predicting the treatment response. The limitation of the study was that the number of samples size with patients undergoing IFN treatment was small. A large cohort of patients undergoing IFN therapy is needed to explain in detail how the SNP rs12979860 and rs8099917 could influence the treatment response in HCV genotype 3 infected population. Our results are the first report from this part of the country providing information about the impact of IL28B genotypes in different HCV infected population groups from eastern and northeastern India. Our results for the first time indicate that for HCV genotype 3 infected patients, CC genotype at rs12979860 is an important predictor for patients to achieve RVR. Additionally our results also emphasized the point that rs12979860 CC host genotype was significantly associated with SVR in genotype 3 infected individuals with high viral load. To best of our knowledge, our data on SNP rs8099917 is the first Indian data within HCV infected population to be reported from this region. In conclusion, it could be said that in the current scenario, where the cost of IFN treatment for HCV is very high to the people of our country where the healthcare system is already overburdened with lack of resources. Therefore, it is the need of the hour to shift our focus to how the treatment mechanisms can be tailor-made to suit every individual’s genetic makeup. A common pathology of pregnancies is early abortion, and 75% of early abortions are associated with embryo implantation failure. Embryo survival within the maternal uterus is affected by many factors, among which humoral homeostasis in the uterine cavity plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, which ultimately affects embryo implantation, differentiation and viability. The early embryo after fertilization appears to have a reduced capacity to regulate homeostasis.
predictor for SVR in treatment of CHC with peg-IFN plus ribavirin. With this aspect in mind, we examined the host genotypes associated with different IFN responses. In patients with RVR, CC genotypes at rs12979860 were present in 77% of the patients whereas the unfavourable CT was present in only 23% of the individuals. Interestingly, none of the patients achieving RVR Talatisamine reported unfavourable TT allele at rs12979860. Similarly, at locus rs8099917, response rates were 73.2% TT, 19.2% TG, followed by 7.6% GG allele. Similar results were obtained in patients with SVR which shows that in 83% of the patients achieving SVR had the favourable CC allele at rs12979860. Interestingly, in patients with relapsed infection it was seen that 66% of the patients had unfavourable CT allele at their rs12979860 locus followed by 34% TT allele. Also at rs8099917, TG genotype was present in 72.4% individuals followed by GG host genotype in 27.6% individuals. Therefore, it could be assumed that favourable genotypes at both rs12979860 and rs8099917 could be important markers for the prediction of the favourable results in patients undergoing IFN therapy in genotype 3 infected patients. Within treatment naive HCV infected individuals, our results showed that the percentage of favourable allele rs12979860 CC and rs8099917 TT was higher; therefore it could be assumed that within our study Mycophenolic acid population the propensity to towards favourable alleles is higher and it could be a valuable input for physicians in predicting the treatment response. The limitation of the study was that the number of samples size with patients undergoing IFN treatment was small. A large cohort of patients undergoing IFN therapy is needed to explain in detail how the SNP rs12979860 and rs8099917 could influence the treatment response in HCV genotype 3 infected population. Our results are the first report from this part of the country providing information about the impact of IL28B genotypes in different HCV infected population groups from eastern and northeastern India. Our results for the first time indicate that for HCV genotype 3 infected patients, CC genotype at rs12979860 is an important predictor for patients to achieve RVR. Additionally our results also emphasized the point that rs12979860 CC host genotype was significantly associated with SVR in genotype 3 infected individuals with high viral load. To best of our knowledge, our data on SNP rs8099917 is the first Indian data within HCV infected population to be reported from this region. In conclusion, it could be said that in the current scenario, where the cost of IFN treatment for HCV is very high to the people of our country where the healthcare system is already overburdened with lack of resources. Therefore, it is the need of the hour to shift our focus to how the treatment mechanisms can be tailor-made to suit every individual’s genetic makeup. A common pathology of pregnancies is early abortion, and 75% of early abortions are associated with embryo implantation failure. Embryo survival within the maternal uterus is affected by many factors, among which humoral homeostasis in the uterine cavity plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, which ultimately affects embryo implantation, differentiation and viability. The early embryo after fertilization appears to have a reduced capacity to regulate homeostasis.
Response guided therapy for CHC patients based on IL28B genotypes
HCV usually induces a robust immune response but it has developed mechanisms to escape immune defense and establish persistent infection. Recent reports indicate that 12.5 million people are infected in India and the number is steadily increasing day by day. As per current guidelines for clinical practice, HCV Anemarsaponin-BIII genotype and HCV RNA levels at baseline are considered to be an important marker before starting the antiviral interferon therapy but studies show that the treatment progression is often marred by side effects which ultimately force the patients to discontinue the therapy. Ge et al., found that Hexamethonium Bromide rs12979860 single nucleotide polymorphism, located 3 kb upstream of the IL28B gene was the strongest host predictor for treatment response in HCV patients infected with genotype 1 strain. Tanaka et al., found rs8099917, another IL28B polymorphism which is located around 8 kb upstream of the IL28B gene, to be the strongest genetic determinant of SVR in HCV genotype 1 infected patients. Initially, most of the studies have concentrated on the HCV genotype 1 as this genotype is more common in western countries. However, the impact of these polymorphisms within genotype 3 HCV infected individuals remains understudied. Reports have also indicated that ethnic differences in the IL28B gene polymorphisms may explain at least in part, the different outcome rates of HCV infection 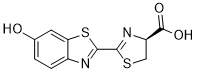 in different population groups. Differences in treatment outcome with respect to antiviral treatment have led the researchers in the present study to ascertain the frequency of IL28B host genotype within different population groups in eastern and north eastern India. The Indian population is ethnically heterogeneous; therefore, genetic variability is expected. Not much data are available about the frequency of host genotype rs12979860 or rs8099917 in India, a study conducted by Sivaprasad et al, amongst south Indian population demonstrated that the proportion of CC allele was higher than the proportion of CT, TT at rs12979860 alleles in the south Indian population, but the study concentrated only on the proportion of the host alleles amongst the healthy individuals. Our study on the other hand analyzed both the healthy individuals as well as HCV infected individuals, to get a clear picture of the genetic disposition of the host genotypes. In this study, analysis of healthy individuals showed that our data is in concordance with the data obtained by Sivaprasad et albut the percentage of favourable CC allele at rs12979860 locus was higher at 73% in contrast to 59.09%. Additionally, our study analyzed the host genetic disposition at both rs12979860 and rs8099917 amongst healthy individuals which was not done elsewhere. The association between IL28B polymorphism and the progression of liver fibrosis is still controversial, as the possible underlying mechanisms are still unknown to us. Within our study population, viral genotype 3 was found to be most widely circulated strain; HCV genotype 3 is reportedly associated with steatosis and rapid progression to HCC. Due to its association with steatosis, we have studied the proportion of IL28B genotypes in HCV infected patients in different stages of advanced liver diseases. We observed that the percentage of unfavourable CT and TG allele were more in these patients as compared to favourable CC and TT allele at rs12979860 and rs8099917 respectively. Several reports indicate strong association between IL28B polymorphism and SVR; the mechanisms are still not properly understood.
in different population groups. Differences in treatment outcome with respect to antiviral treatment have led the researchers in the present study to ascertain the frequency of IL28B host genotype within different population groups in eastern and north eastern India. The Indian population is ethnically heterogeneous; therefore, genetic variability is expected. Not much data are available about the frequency of host genotype rs12979860 or rs8099917 in India, a study conducted by Sivaprasad et al, amongst south Indian population demonstrated that the proportion of CC allele was higher than the proportion of CT, TT at rs12979860 alleles in the south Indian population, but the study concentrated only on the proportion of the host alleles amongst the healthy individuals. Our study on the other hand analyzed both the healthy individuals as well as HCV infected individuals, to get a clear picture of the genetic disposition of the host genotypes. In this study, analysis of healthy individuals showed that our data is in concordance with the data obtained by Sivaprasad et albut the percentage of favourable CC allele at rs12979860 locus was higher at 73% in contrast to 59.09%. Additionally, our study analyzed the host genetic disposition at both rs12979860 and rs8099917 amongst healthy individuals which was not done elsewhere. The association between IL28B polymorphism and the progression of liver fibrosis is still controversial, as the possible underlying mechanisms are still unknown to us. Within our study population, viral genotype 3 was found to be most widely circulated strain; HCV genotype 3 is reportedly associated with steatosis and rapid progression to HCC. Due to its association with steatosis, we have studied the proportion of IL28B genotypes in HCV infected patients in different stages of advanced liver diseases. We observed that the percentage of unfavourable CT and TG allele were more in these patients as compared to favourable CC and TT allele at rs12979860 and rs8099917 respectively. Several reports indicate strong association between IL28B polymorphism and SVR; the mechanisms are still not properly understood.
Histopathological examination has revealed increased numbers of vessels concentration of Angpt-2
Praeruptorin-B Angpt-2 expression directly within the tumor by fluorescent immunohistochemistry from human tissue samples. We found increased circulating levels of Angpt-2 in patients with CC compared to those with non-malignant pathologies. Our data indicate that Angpt-2 is useful as an additional novel marker. More importantly the data indicate a putative mechanistic involvement of Angpt-2 in tumor angiogenesis and might therefore represent a promising candidate for future therapeutic intervention. However, this aspect is clearly beyond the scope of the current project but warrants further investigation. We assume that elevated Angpt-2 in the serum reflects its potent – but most likely unspecific �C mediator function in tumor neoangiogenesis as it has been demonstrated for other entities. For the first time, we demonstrate that Angpt-2 is detectable in bile of CC patients. However, its pathophysiological role in bile is completely unknown. We hypothesize that in the sense of a “demand and supply” strategy the tumor cells might be able to produce Angpt-2 to maintain neoangiogensis at a high level. The detection of Angpt-2 in bile might be the result of tumor involvement of the large bile ducts and secretion of Angpt-2 from tumor vessels. A passive diffusion of Angpt-2 from blood vessels into the bile seems unlikely as no correlation was found for serum and bile Angpt-2 levels. Taking the current Angpt/Tie2 knowledge in healthy conditions into account, one would assume that the tumor vasculature is the primary source of Angpt-2 biosynthesis as Angpt-2 is synthesized in the endothelium. With respect to this theoretical assumption and our earlier observation that Angpt-2 is also detectable in the bile we performed immunohistochemical stainings for Angpt-2. Of note, our histological data did show that it is indeed the vasculature where Angpt-2 is expressed in biopsies from human CC samples. PSC patients are at special risk to develop CC and need accurate monitoring. In many patients, PSC is complicated by CC development despite regular surveillance. Consequently, new diagnostic approaches are required. However, Angpt-2 measurement did not help to detect CC/PSC in our cohort. Unfortunately, serum samples were not available for all patients which is a limitation of our study. Therefore we measured Angpt-2 in additional serum samples without concomitant bile specimens to provide sufficient data for statistical analysis. In summary, we show that Angpt-2 is significantly elevated in patients with CC and has a higher AUC value in ROC analysis than CA 19-9 in our cohort. More importantly, Angpt-2 is expressed in the tumor vasculature and thus is of interest for the diagnosis 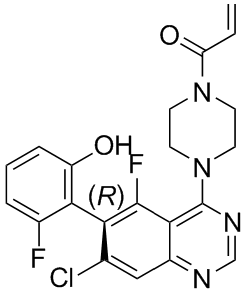 and therapy in patients with CC. Tendinopathy is a common overuse injury, prevalent among both athletes and workers. The disorder is often considered a mechanically driven pathology, as repetitive or forceful loading of tendons are well established risk factors. Repetitive strain and shear are thought to induce matrix degeneration in tendon tissue, making the tissue susceptible to damage and eventually to overuse injury. However, the mechanisms which precede the development of symptomatic injury have not been fully described but are felt to be multifactorial, with repetitive strain being an important risk Coptisine-chloride factor. There is evidence of extensive new blood vessel growth in most types of tendinopathy, including Achilles, patellar and lateral epicondyle tendinopathies, as well as the rotator cuff.
and therapy in patients with CC. Tendinopathy is a common overuse injury, prevalent among both athletes and workers. The disorder is often considered a mechanically driven pathology, as repetitive or forceful loading of tendons are well established risk factors. Repetitive strain and shear are thought to induce matrix degeneration in tendon tissue, making the tissue susceptible to damage and eventually to overuse injury. However, the mechanisms which precede the development of symptomatic injury have not been fully described but are felt to be multifactorial, with repetitive strain being an important risk Coptisine-chloride factor. There is evidence of extensive new blood vessel growth in most types of tendinopathy, including Achilles, patellar and lateral epicondyle tendinopathies, as well as the rotator cuff.
Different developmental stages using traditional chromatographic techniques and mass spectrometry
Some limitations of this study should be consideration. First, long term follow-up data are lacking. Further studies are needed to determine whether serum IGF-1 levels predicts long term outcomes after a stroke in our population. Second, serum IGF-1 levels were only measured once at admission, this study yielded no data regarding when and how long IGF-1 is elevated in these patients. Thus, additional measurements in the days after would have been of interest. Furthermore, biological effects and bioavailability of IGF-1 are modulated through IGFBPs, which control IGF-1 access to cell surface receptors. Unfortunately, we did not have IGFBPs available, and therefore our Procyanidin-B1 results do not fully represent biologically active IGF-1. Finally, data derived from a single-centre study always need to be replicated in larger multicentre studies. The interrogation of biological systems with secondary ion mass spectrometryhas seen significant growth over the last decade.This relatively newfound application of a surface technique traditionally limited to the study of inorganic and small molecule analytes is largely derived from the advent of larger, cluster primary ion probeswhich provide enhanced secondary ion yields of molecular and fragment ions from biological samples. While the use of traditional time of flightand magnetic sector based methodologies have intrinsic advantages for the in situ analysis of surfaces, the complexity and number of components usually encountered in the analysis of biological systems warrant the coupling of these new sources to high mass accuracy and resolution analytical devices for direct identification of the molecules of interest.In particular, this requirement grows out of the need for improved identification certainty for molecular ions generated from biological samples, which are substantially more complex relative to semiconductor and polymer-based applications, where the number of sample components is limited and the analyte of interest is typically predetermined. Previous mass spectrometry imaging studies have shown the advantages of correlating spatial information with molecular composition for the study of a variety of biological systems.A common drive has been the search for biological models and better interrogation probes with higher spatial resolution and improved molecular identification. To this end, we used Dictyostelium discoideum as a biological model for evaluating the performance of two different mass spectrometry imaging approaches. D. discoideum cells are eukaryotic cells that normally live on soil surfaces and eat bacteria.An interesting feature of their biological cycle is that when the cells overgrow their food supply and starve, they aggregate together in dendritic streams to form groups of,20,000 cells. The aggregated cells eventually form a fruiting body consisting of a 1�C2 mm tall stalk supporting a mass of spore cells which  can then be dispersed by the wind to start new colonies. Gomisin-D Because soil surfaces are exposed to rain water, the cells can survive and undergo development in water. This feature makes D. discoideum a good model for in situ mass spectrometry imaging since it does not require the use of cleaning protocols that can potentially compromise the spatial information. In addition, this cell averages 10 mm in size, which is at the fron their distribution.
can then be dispersed by the wind to start new colonies. Gomisin-D Because soil surfaces are exposed to rain water, the cells can survive and undergo development in water. This feature makes D. discoideum a good model for in situ mass spectrometry imaging since it does not require the use of cleaning protocols that can potentially compromise the spatial information. In addition, this cell averages 10 mm in size, which is at the fron their distribution.