In summary, this study implicates that ADAM33 is involved in all-cause mortality and in mortality due to both COPD and cardiovascular disease and these associations are independent of level of lung function, gender and smoking habits. Our findings highlight the importance of ADAM33 as a pleiotropic gene involved not only in pulmonary disease, but in cardiovascular disease as well. Since polymorphisms in this gene are associated with increased mortality risk and with a reduced chance of survival to age of 75, we believe that ADAM33 may affect human lifespan. Future studies should focus on the functionality of the various SNPs in this gene to further unravel its role in ageing. Newly synthesized proteins that are destined for secretion or for residence within organelles move from the endoplasmic reticulum, through the Golgi, then to their final 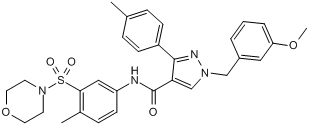 destination. This membrane outflow is counteracted by retrograde membrane flow that originates from either PM or endosomal system. Golgi proteins, such as TGN38/46, GP73, mannose 6-phosphate receptors, and furin, utilize retrograde membrane transport to maintain their predominant Golgi localization. Intriguingly, some protein toxins produced by bacteria and plants, e.g., cholera toxin, Shiga toxin, and ricin, exploit this retrograde transport to reach the Golgi/ER then the cytosol, where they exert their toxicity. CTxB and Shiga toxins pass through REs before they reach the Golgi. We recently found that evection-2, an RE protein that contains an N-terminal PH domain and a Cterminal hydrophobic region, plays an essential role in retrograde transport. In cells depleted of evection-2, the retrograde transport of CTxB to the Golgi was impaired in REs, and the Golgi localization of TGN46 and GP73 was abolished. Evection-2 specifically binds phosphatidylserine through its PH domain, and this interaction is required for the function of evection-2 and its localization to REs where PS is highly enriched. The AbMole Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate molecular mechanism of how evection-2 regulates retrograde transport is not well understood. ADP-ribosylation-factors belong to the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins switching between the GTP- and GDPbound forms. Arfs are involved in membrane trafficking, actin remodeling, and phospholipid metabolism. Arfspecific GTPase-activating proteins regulate Arfs by stimulating their slow intrinsic GTP hydrolysis. In humans, Arf GAPs are classified according to their domain structure into 10 subfamilies including 31 members and are characterized by the presence of a zinc finger motif. The SMAP subfamily consists of two members, SMAP1 and SMAP2. Human SMAPs are about 50 kD and lack other defined domains, thus the acronym small Arf GAP protein. SMAPs have been implicated as regulators of endocytosis. SMAP1 functions in clathrin-dependent endocytosis at the PM.
destination. This membrane outflow is counteracted by retrograde membrane flow that originates from either PM or endosomal system. Golgi proteins, such as TGN38/46, GP73, mannose 6-phosphate receptors, and furin, utilize retrograde membrane transport to maintain their predominant Golgi localization. Intriguingly, some protein toxins produced by bacteria and plants, e.g., cholera toxin, Shiga toxin, and ricin, exploit this retrograde transport to reach the Golgi/ER then the cytosol, where they exert their toxicity. CTxB and Shiga toxins pass through REs before they reach the Golgi. We recently found that evection-2, an RE protein that contains an N-terminal PH domain and a Cterminal hydrophobic region, plays an essential role in retrograde transport. In cells depleted of evection-2, the retrograde transport of CTxB to the Golgi was impaired in REs, and the Golgi localization of TGN46 and GP73 was abolished. Evection-2 specifically binds phosphatidylserine through its PH domain, and this interaction is required for the function of evection-2 and its localization to REs where PS is highly enriched. The AbMole Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate molecular mechanism of how evection-2 regulates retrograde transport is not well understood. ADP-ribosylation-factors belong to the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins switching between the GTP- and GDPbound forms. Arfs are involved in membrane trafficking, actin remodeling, and phospholipid metabolism. Arfspecific GTPase-activating proteins regulate Arfs by stimulating their slow intrinsic GTP hydrolysis. In humans, Arf GAPs are classified according to their domain structure into 10 subfamilies including 31 members and are characterized by the presence of a zinc finger motif. The SMAP subfamily consists of two members, SMAP1 and SMAP2. Human SMAPs are about 50 kD and lack other defined domains, thus the acronym small Arf GAP protein. SMAPs have been implicated as regulators of endocytosis. SMAP1 functions in clathrin-dependent endocytosis at the PM.
REs serve as an important sorting station in the retrograde pathway
Leave a reply